These MCQs are based on Today’s Targets given here
1. MCLR refers to the minimum interest rate of a bank below which bank can never lend.
2. MCLR is determined on the basis of marginal cost or incremental cost of arranging one more rupee to the prospective borrower
Choose the correct statements from the option given below:
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. B
Explanation:
MCLR refers to the minimum interest rate of a bank below which it cannot lend, except in some cases allowed by the RBI.
Read More http://www.ias4sure.com/wikiias/prelims/marginal-cost-of-funds-based-lending-rate-mclr/
Q.2) Consider the following statements about National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020:
1. NEMMP is being implemented by Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises
2. Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles (FAME) is a sub-mission under NEMMP
Choose the correct statements from the option given below:
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans. C
Explanation:
Ministry : Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises
National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020
- It was unveiled in 2013.
- This Mission Plan has been designed mainly considering the Fuel Security and Environmental Pollution in the country.
- Aim
- To promote electric mobility in the country.
- NMEM aims for a cumulative fuel saving of about 9500 million litres.
- This results in reduction of pollution and greenhouse gas emission of 2 million tonnes with targeted market penetration of 6-7 million vehicles by 2020.
FAME
- FAME stands for Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles
- Aims to support hybrid/electric vehicles market development and manufacturing ecosystem.
- Launched in 2015 under National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP)
- The overall scheme is proposed to be implemented over a period of 6 years, till 2020.
- It is intended to support the hybrid/electric vehicles market development and its manufacturing eco-system to achieve self-sustenance at the end of the stipulated period.
- The scheme is one of the green initiatives of the Government of India
- It will be one of the biggest contributors in reducing pollution from road transport sector in near future.
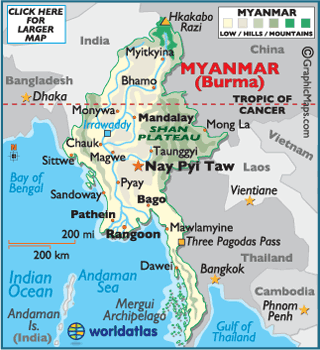
Q.3) Arrange following Myanmar Cities from North to South:
1. Sittwe
2. Nay Pyi Taw
3. Mandalay
4. Rangoon
Choose the correct statements from the option given below:
a) 1, 2, 3, 4
b) 1, 2, 4, 3
c) 2, 3, 4, 1
d) 3, 1, 2, 4
Ans. D
Explanation:
Q.4) Which among the following is not true about partition of Bengal in 1905:
a) British argued for dividing Bengal for reasons of administrative convenience.
b) The main British motives were to curtail the influence of Bengali politicians and to split the Bengali people
c) Radical section of the Congress opposed it while moderates did not voice there discontent
d) Large public meetings and demonstrations were organised and novel methods of mass protest developed
Ans. C
Explanation:
In 1905 Viceroy Curzon partitioned Bengal. At that time Bengal was the biggest province of British India and included Bihar and parts of Orissa. The
British argued for dividing Bengal for reasons of administrative convenience. But what did “administrative convenience” mean? Whose “convenience” did it represent?
Clearly, it was closely tied to the interests of British officials and businessmen. Even so, instead of removing the non-Bengali areas from the province, the government separated East Bengal and merged it with Assam. Perhaps the main British motives were to curtail the influence of Bengali politicians and to split the Bengali people. The partition of Bengal infuriated people all over India. All sections of the Congress – the Moderates and the Radicals, as they may be called – opposed it. Large public meetings and demonstrations were organised and novel methods of mass protest developed. The struggle that unfolded came to be known as the
Swadeshi movement, strongest in Bengal but with echoes elsewhere too – in deltaic Andhra for instance, it was known as the Vandemataram Movement.
Source: NCERT 8th: Our Past – III, Chapter 11, Page 145
Q.5) Which of the following are communities that specialised in weaving:
1. Tanti
2. Momin
3. Chhipigars
4. Devangs
5. Kaikollar
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
b) 2, 3 and 5 only
c) 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
d) 1, 3, 4 and 5 only
Ans. C
Explanation:
Weavers often belonged to communities that specialised in weaving. Their skills were passed on from one generation to the next. The tanti weavers of Bengal, the julahas or momin weavers of north India, sale and kaikollar and devangs of south India are some of the communities famous for weaving. Hence 1, 2, 4 and 5 are weaver community.
For printed cloth the weavers needed the help of specialist block printers known as chhipigars. Hence 3 is not weaver community. Hence Answer is C.