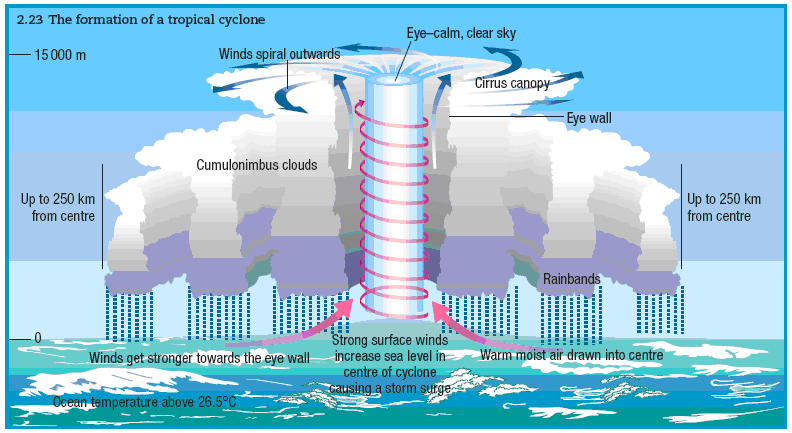
What is a Tropical Cyclone?
- A Cyclone represents a rotating, organized system of clouds and thunderstorms that originates over tropical or subtropical waters and has closed low-level circulation.
- Most large scale cyclonic circulations are centred on areas of low atmospheric pressure.
- Based on their latitude, the cyclones may be tropical cyclones or temperate cyclones (extra-tropical cyclones).
- The tropical cyclones rotate anti-clockwise in the northern hemisphere and are classified into types viz.
- Tropical Depression (maximum sustained winds of 38 mph or less);
- Tropical Storm (maximum sustained winds of 39 to 73 mph);
- Hurricane (maximum sustained winds of 74 mph) and
- Major hurricane (maximum sustained winds of 111 mph).
- Hurricanes are called typhoons in western North Pacific, while similar storms in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean are called cyclones.
Tropical Cyclones in Indian Ocean
- Tropical cyclones between east of the Horn of Africa and west of the Malay Peninsula are most common from April to December, with peaks in May and November in the Indian Ocean.
Naming of Tropical Cyclones:
They classified into three main groups, based on intensity:
- tropical depressions,
- tropical storms, and
- a third group of more intense storms, whose name depends on the region:
- North-West Pacific – Typhoon
- North-East Pacific and Atlantic – Hurricane
- Indian Ocean- Cyclone