Narmada River:
-
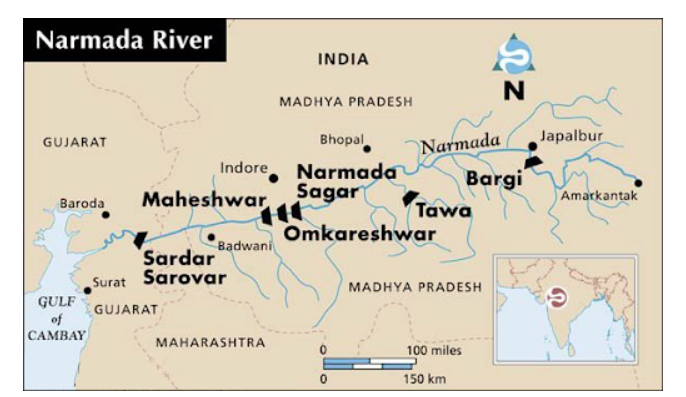
Narmada is the largest west flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south.
-
It rises from Maikala range near Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh.
-
It drains a large area in Madhya Pradesh besides some areas in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
-
The river near Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh) forms the DhuanDhar Falls.
-
There are several islands in the estuary of the Narmada of which Aliabet is the largest.
-
Major Tributaries: Hiran, Orsang, the Barna and the Kolar.
-
The major Hydro Power Projects in the basin are Indira Sagar, Sardar Sarovar etc.
-
Narmada Bachao Andolan (NBA):
-
It is an Indian social movement spearheaded by native tribes (adivasis), farmers, environmentalists and human rights activists against a number of large dam projects across the Narmada River.
-
Sardar Sarovar Dam in Gujarat is one of the biggest dams on the river and was one of the first focal points of the movement.
-
Previous Year Questions:
Q 1.) The Narmada river flows to the west, while most other large peninsular rivers flow to the east. Why? (2013)
-
It occupies a linear rift valley.
-
It flows between the Vindhyas and the Satpuras.
-
The land slopes to the west from Central India.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (a)