- It is a wind-sensing satellite launched by European Space Agency (ESA).
- The satellite is named Aeolus after guardian of wind in Greek mythology.
- It will be placed at altitude of 320km above the Earth.
- It is part of the Copernicus project, a joint initiative of European Union (EU) and European Space Agency (ESA) to track environmental damage and aid disaster relief operations.
- Aeolus satellite is equipped with single instrument Doppler wind lidar (named Aladin), which is an advanced laser system designed to accurately measure global wind patterns from space.
- It will probe lower layers of atmosphere, down to altitude of about 30 km to yield vertical profiles of wind and information on aerosols and clouds.
- Significance: Aeolus satellite will provide much-needed data to improve quality and accuracy of weather forecasting. It will help to improve understanding of working of atmosphere dynamics and contribute to climate change research.
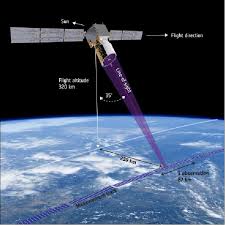
Working of Doppler LIDAR
- It transmits short, powerful pulses of laser light toward Earth in ultraviolet (UV) spectrum.
- Particles in air (such as moisture, dust, gases) scatter small fraction of that light energy back to transceiver, where it is collected and recorded.
- The delay between outgoing pulse and so-called backscattered signal reveals wind’s direction, speed and distance travelled.