Context:
-
Recent turmoil and farmers protests which can be attributed to hasty passage of farmers bills without following due legislative process.
-
Legislative scrutiny of bills through committees results in more comprehensive, representative and acceptable laws and lack of it results in dissatisfaction and non-acceptance as happening in case of farm laws.
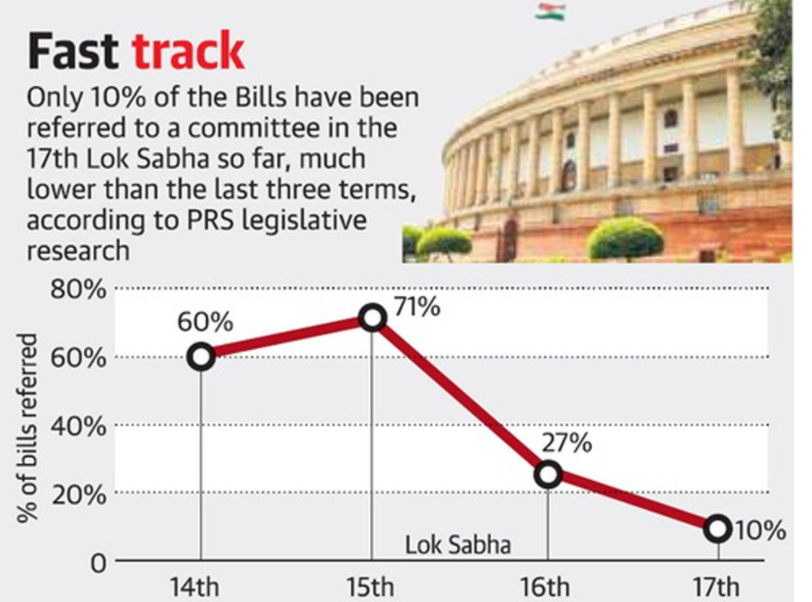
Facts:
-
Only 10% of the Bills have been referred to a committee in 17th LS.
Parliamentary committees:
-
Historical background:
-
British Parliament: following it since the 16th
-
Colonial period: Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms introduced it, and the Central Legislative Assembly had set up three committees.
-
-
Post-independence: Prior to the formation of Standing Committees, the Parliament used to appoint select committees and joint select committees for detailed scrutiny of important legislations.
-
Process followed now:
-
Rules of the Houses provides that speaker/chairman has the discretion to whether send a bill to a standing committee or not.
-
If sent, the committee does detailed scrutiny of the concerning bill and sends their recommendations on improvements to be made in the Bills to the Houses.
-
While undertaking such scrutiny, the committees invite various stakeholders to place their views before them, resulting in more representative laws.
-
Benefits:
-
A tool of consensus making: resulting in deepening of parliamentary democracy and helps in getting expert views on the matter as parliamentarians are considered layman.
-
Improves the pieces of legislation: through detailed scrutiny by various committees.
-
E.g. the Goods and Services Tax Bill, The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Bill.
-
-
Capacity to harmonise contradictions: Members work in non-party fashion in these committees, hence less prone to vested political interests.
Concerns:
-
Misuse of discretionary powers by presiding authority by not sending important bills to committees for detailed scrutiny.
-
Adversarial politics: has resisted the government from introducing the critical bills to the committees.
Conclusion: Systems of Parliament are inclusive, and these parliamentary committees provide a platform to members to rise above party line and work towards formulating sound laws.