Facts:
- The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education of Indian has registered an increase from 10% in 2004-05 to 25.8% in 2017-18according to latest All India Higher Education Survey (AIHES) released by HRD Ministry.
- India is aiming to attain GER of 30% by 2020, but it is still far behind countries like China with GER of 43.39% and US with 85.8%.
- GIAN – project to rope in eminent scholars from abroad to teach at Centrally-funded institutions (Global Initiative of Academic Network)
The report on the annual status of higher educational universities and colleges in India pointed out that, states that lay more emphasis on the quality and depth of their higher education are economically better placed than those that do not. Analyse the reasons behind this linkage? What initiatives must the states take to improve higher education in the country? (200 Words)
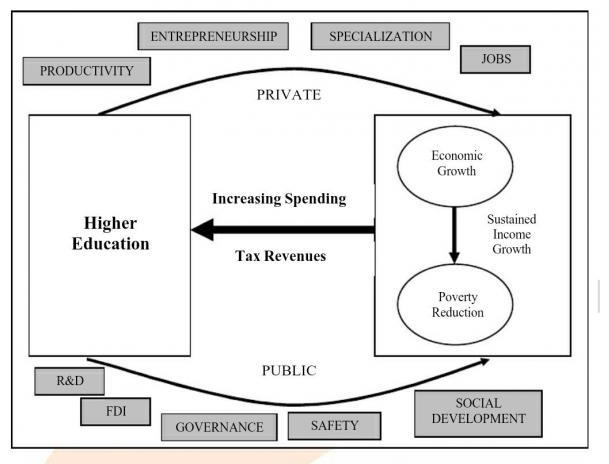
Knowledge based competition within a globalising economy is prompting a fresh consideration of the role of higher education in economic development and growth There is a positive correlation between investment in higher education and economic growth of a state (directly and indirectly)
- It helps in rapid industrialization by providing manpower with professional, Technical and managerial skills.
- In present context of transformation of nations into knowledge economies and knowledge societies, it provides not just educated workers but knowledge workers to the growth of economy
- It creates attitudinal changes necessary for the socialization of individuals and overall transformation of society
- Higher education contributes through the ―production of knowledge‖ and that largely takes place within major universities and their research
- Helps in creation of new technology which contributes to the economy of the state
- Higher education leads to economic growth through both private and public channels. Higher earnings for well-educated individuals raises tax revenues for governments and eases demands on state finances. They also translate into greater consumption, leading to greater production and a demand-driven economy.
- In addition, the larger tax base reduces the tax pressure on low-income members
- A more educated workforce gives a higher output per worker in 2 ways
- Higher education adds more skill to workforce
- Increases the capacity to innovate
- The growth of science-based industries also means that economic development depends on highly educated and scientifically trained labour
Initiatives to improve higher education :
- Instead of funding public colleges and universities based on enrollments, states should use a formula that pays institutions for success in key areas like progress toward and completion of degrees and credentials, research
- Promoting technical and vocational universities
- Promoting private investment in higher education
- Establishment of more centers of excellences.
- International collaboration and student exchange programmes
- Promoting industrial participation in designing different vocational and technical courses so that demand based skills are acquired.
Thus along with promoting primary and secondary education, there is also a need for states to promote higher education which brings not only a higher economic growth but also social and other returns.
“The perverse kind of political interference that routinely takes place in higher education is one of the primary reasons that the best of India’s colleges and universities lag behind.” Examine the causes of political interference, its implications and solutions to the problem. (200 Words)
Political interference is not new to the education system especially higher education. The FYUP of the Delhi University is a clear evidence of this. There are many causes for this problem:
- The one-upmanship of the executive, corruption, student’s connection with political groups like ABVP etc.
- The lack of transparency, accountability among the hierarchy of the higher education system allowing political interference.
- Ideological differences of the parties pushing for changes in discipline like history etc.
- Accreditation system, allotting deemed or other status to a college etc. are ridden with lobbying from the University or college authorities pulling political influence into the system.
- Issues in appointments, system of functioning of autonomous bodies like IITs, IIMs etc. drawing comments and opinions from politicians.
Implications of the political interference are:
- lack of competence, collaboration and coordination in the higher education,
- failure in governance of the universities or colleges leading to reduction in standards,
- performance of students,
- No vibrant growth like foreign universities with multiple disciplines and autonomy of subjects/courses,
- rise in corruption, personal rivalry among authorities etc.
It is good governance, transparency, accountability which must be ensured, sufficient autonomy and enforcing discipline among the university authorities coupled with reforms like freedom to choose courses, refrain from making college issues political, better financial autonomy which are needed for efficient functioning of Higher education system in India.
An intense debate is going on the Union government’s proposal to revive the Central Universities Act of 2009 which will require the Central universities to follow a common admission procedure and common syllabus. Analyse the issue and critically comment if following a common syllabus is good for higher education sector in India. (200 Words)
Higher education is going through a difficult phase on various fronts namely both quality as well as quantity along with research and innovation to name a few. As a result no Indian University is in the list of top 200 universities in the world. In this perspective Union government have proposed to revive the Central Universities Act of 2009
This Act has the following objectives:
- Mandate a common admission procedure and common syllabus for all universities.
- Transfer policy for faculty as in they can be transferred between different universities.
- It may mandate all universities to initiate CBCS.
- Provide an opportunity to the below average universities to improve upon their quality
Advantages:
- They make it feasible to measure and rank universities.
- Since, most of the universities in metropolitan cities are better served with distinguished faculty and expertise, it provides a level playing field to all universities due to faculty mobility
- Framing syllabus to meet industry requirements, focus on skill development of students
- Students have to fill single form instead of plethora of forms and have to prepare for single test with on specified syllabus.
- New universities will have greater chance of getting good students and faculty due to provisions of mobility
- All universities have to complete their accreditation with NAAC. This is a good step as it will ensure adherence to required specification.
- Provisions for a Central university teacher recruitment board that will set standards for assistant professor after qualifying NET. This will ensure quality of teachers as required qualification will be an improvement of minimum being NET qualified which is currently in practice.
- Academic and research activities will be subjected to external review. Students will be allowed to participate in this review.
Issues:
- The act centralises and homogenises education completely ignoring the specialisation and uniqueness and diversity of each university. Universities in N-E are created to cater to students of that region, JNU was created to promote national values, humanism etc., DU was created to provide education along diverse subjects, common syllabus will take away special character of these universities
- Transfer policy is detrimental to academics. Research requires long time presence of the faculty. Secondly, it has potential to silence dissent of faculty. Transfer of faculty will increase the possibility of vindictiveness as it is a punitive measure to silence the dissent and independent voices.
- Further this will be impact research and innovation which is already very low in the country. Faculties specializing in different fields and researchers will lose the zeal to practice and promote their field with enthusiasm owing to limited domain as a result of common syllabus. This will further impact and deter the growth of higher education on qualitative aspects.
- Common syllabus will do more harm than good. Indian institutions presently are termed as “islands of excellence and oceans of mediocrity” which might turn into “oceans of mediocrity” as a result of common syllabus. This will result in further lowering the qualitative aspects of education and its excellence.
- Loss of Autonomy again due to common syllabus.
- Due to 35% of vacant teaching posts, universities are already breaching the global teacher-pupil ratio; mobility of students will not be helpful in this case
What are the challenges private universities have posed to higher education in India? Should they be strictly regulated? Critically comment. (200 Words)
Challenges posed by private universities:
- arbitrary admission criteria, capitation fees and vested interests dominate these universities
- they spread misinformation among students about recognition, faculty, course structure and quality. These leads to fake degrees and unrecognised qualifications causing problems for students when they pass out and enter job market.
- Political patronage and nexus promotes setting up of these universities flouting standard norms and criteria.
- Poor quality of teaching, infrastructure, labs and practical impedes genuine learning at these universities
- The financial criteria denies the poor and underprivileged students admissions leading to inequity in education
Regulation:
- NCHER bill needs to be passed to setup a strong assessment, accreditation, rating and regulatory framework in the country. Universities not adhering to prescribed standards should be de-recognised while strong regular monitoring should be done for the rest
- Grievance redressal, counselling, prior information, strict checking on correctness of online ad contents, quick action on complaints and monitoring of financial irregularities and frauds are some steps which need to be urgently taken.
- For accreditation: NAAC and NBA (National Board of Accreditation) could be strengthened